[Data Analysis] SQL Recipe for Data Analysis Tutorial #2 - Manipulating a single value
Goal
- Studying SQL for data analysis
- Practicing chapter 3rd in the book
- Studying SQL for Manipulating data
Practice
Book for studying
| Title | 데이터 분석을 위한 SQL 레시피 |
|---|---|
| Author | Nagato Kasaki, Naoto Tamiya |
| Translator | 윤인성 |
| Publisher | 한빛미디어 |
| Chapter | 3 |
| Lesson | 5 |
- I’m gonna study basic SQL syntax and functions for data analysis
- I’m gonna study how to manipulate from a single value to multiple tables
- I’m gonna try to load test data on PostgreSQL and execute queries in the book
3.5. Manipulating a single value
3.5.1. Replace the code value with a label
- To replace the code value with some label to enhance the readability
Make sample table and data
- Create user master table which has 3 colums
- register_device column has 3 types of code data
- 1: Desktop
- 2: Smartphone
- 3: Application
-- Create user master table
CREATE TABLE mst_users(
user_id varchar(255)
, register_date varchar(255)
, register_device integer
);
-- Insert sample data
INSERT INTO mst_users
VALUES
('U001', '2020-08-26', 1)
, ('U002', '2016-08-26', 2)
, ('U003', '2016-08-27', 3)
;
commit;
-- Select sample data
SELECT *
FROM mst_users
;
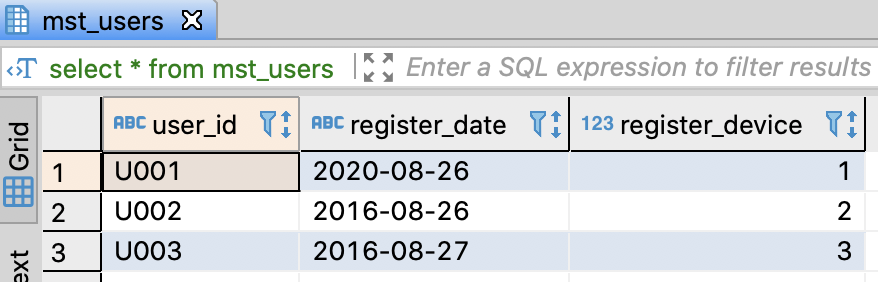
Execute Query
- Use CASE clause
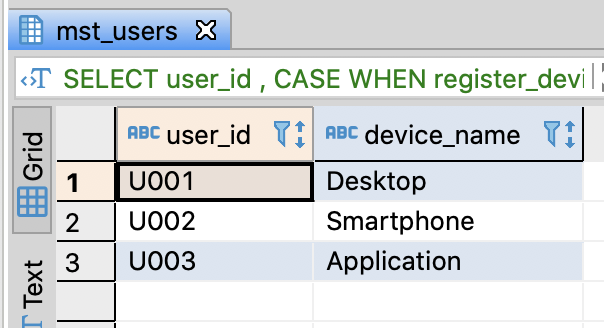
-- Query for replacing code with label
SELECT user_id
, CASE WHEN register_device = 1 THEN 'Desktop'
WHEN register_device = 2 THEN 'Smartphone'
WHEN register_device = 3 THEN 'Application'
-- ELSE (Default)
END AS device_name
FROM mst_users
;
3.5.2. Extract some factors from URL
Create access log table
- This table has 3 columns such as referrer and url
- There are several databases that have URL data type
-- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS access_log ;
-- Create access log table
CREATE TABLE access_log (
stamp varchar(255)
, referrer text
, url text
);
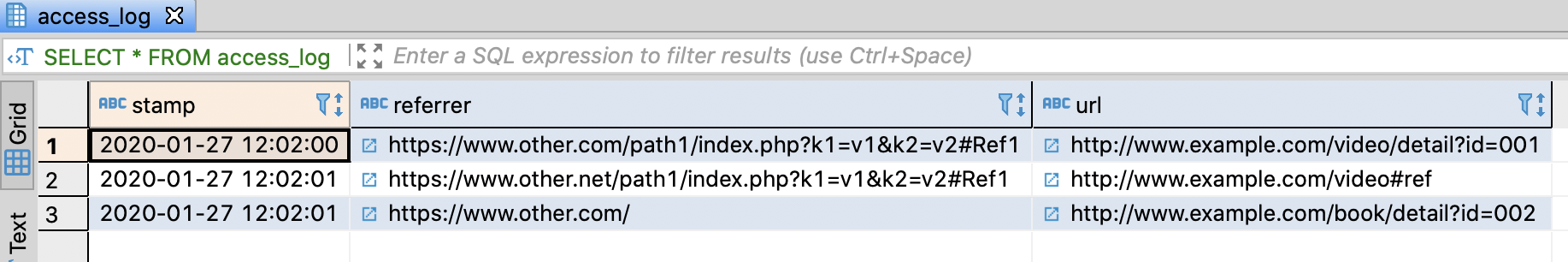
-- Insert sample data
INSERT INTO access_log
VALUES
('2020-01-27 12:02:00', 'https://www.other.com/path1/index.php?k1=v1&k2=v2#Ref1', 'http://www.example.com/video/detail?id=001')
, ('2020-01-27 12:02:01', 'https://www.other.net/path1/index.php?k1=v1&k2=v2#Ref1', 'http://www.example.com/video#ref' )
, ('2020-01-27 12:02:01', 'https://www.other.com/' , 'http://www.example.com/book/detail?id=002' )
;
commit;
-- Select sample data
SELECT *
FROM access_log
;
Extract the domain of a referrer
- Furthermore, Hive and BigQuery have the function hadling URL
- Unfortunately, you have to extract the domain by using regex expression if you are using other databases
HTTP referer : (a misspelling of referrer[1]) is an optional HTTP header field that identifies the address of the webpage (i.e. the URI or IRI) which is linked to the resource being requested. By checking the referrer, the new webpage can see where the request originated
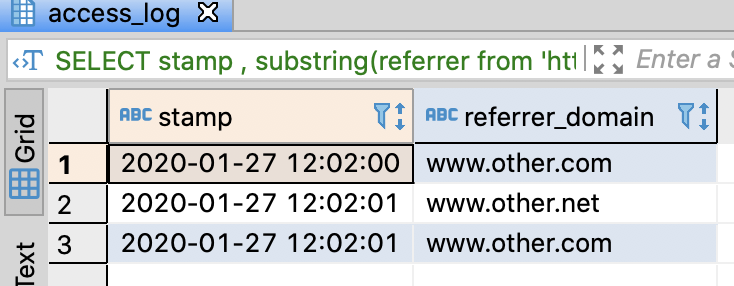
-- Extract the domain of referrer
SELECT stamp
, substring(referrer from 'https?://([^/]*)') AS referrer_domain
-- if Redshift
-- , regexp_replace(regexp_substr(referrer, 'https?://[^/]*'), (https?://', '') AS referrer_domain
-- if Hive or SparkSQL
-- , parse_url(refferer, 'HOST') AS referrer_domain
-- if BigQuery
-- , host(referrer) AS referrer_domain
FROM access_log
;
Extract the path and query parameters from URL
-- Extract the path and query parameters from URL
SELECT stamp
, url
, substring(url from '//[^/]+([^?#]+)') AS path
, substring(url from 'id=([^%]*)') AS id
-- if Redshift
-- , regexp_replace(regexp_substr(referrer, '//[^/]+([^?#]+)'), '//[^/]+', '') AS path
-- , regexp_replace(regexp_substr(referrer, 'id=([^%]*)', 'id=', '') AS id
-- if Hive or SparkSQL
-- , parse_url(refferer, 'PATH') AS path
-- , parse_url(refferer, 'QUERY') AS id
-- if BigQuery
-- , parse_url(url, '//[^/]+([^?#]+)') AS path
-- , parse_url(url, 'id=([^%]*)') AS id
FROM access_log
;
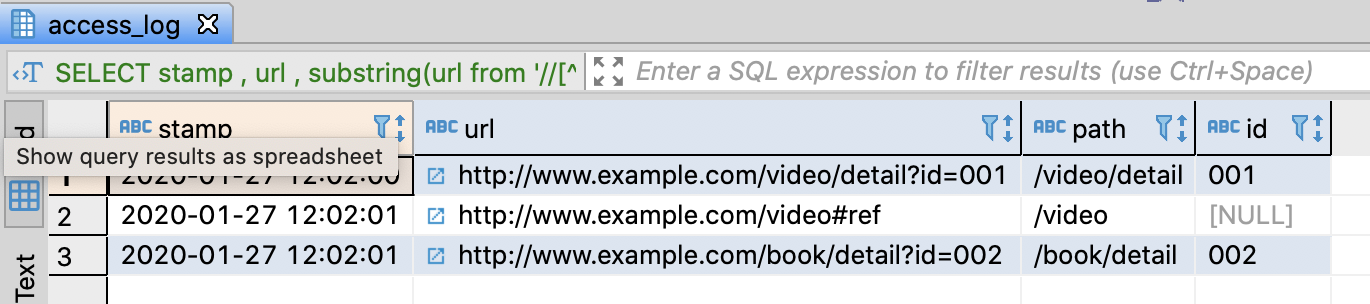
3.5.3. Separate string into array
- There are many cases that you have to separate string by comma or space or anything else
- I’m gonna show path level from URL in access_log table
-- Extract path hierarchy
SELECT stamp
, url
, split_part(substring(url from '//[^/]+([^?#]+)'), '/', 2) AS path1
, split_part(substring(url from '//[^/]+([^?#]+)'), '/', 3) AS path2
-- if Redshift
-- , split_part(regexp_replace(regexp_substr(url, '//[^/]+([^?#]+'), '//[^/]+([^?#]+', ''), '/' 2) AS path1
-- , split_part(regexp_replace(regexp_substr(url, '//[^/]+([^?#]+'), '//[^/]+([^?#]+', ''), '/' 3) AS path2
-- if Hive or SparkSQL (Index number starts from 0)
-- , split(parse_url(url, 'PATH'), '/')[1] AS path1
-- , split(parse_url(url, 'PATH'), '/')[2] AS path2
-- if BigQuery
-- , split(regexp_extract(url, '//[^/]+([^?#]+)'), '/')[SAFE_ORDINAL(2)] AS path1
-- , split(regexp_extract(url, '//[^/]+([^?#]+)'), '/')[SAFE_ORDINAL(3)] AS path2
FROM access_log
;
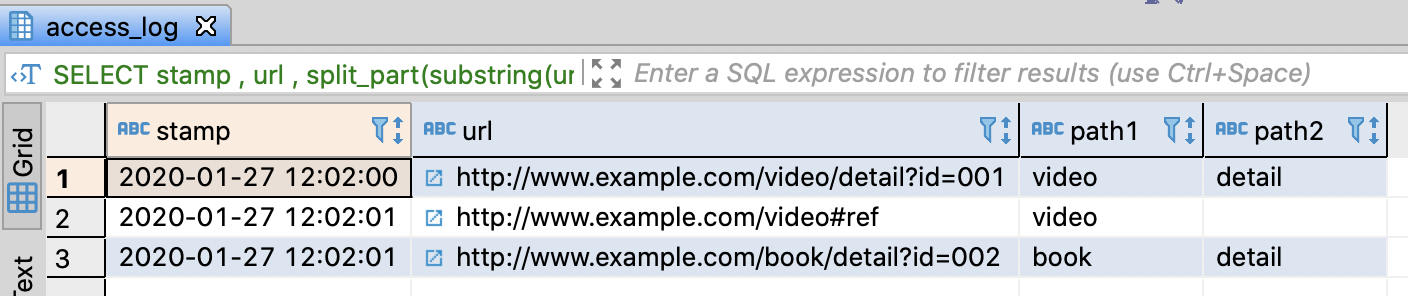
Redshift doesn’t support array data type officially. However, you can get Nth factor from separated string through split_part function
Generally, array index is 1 based, while array index is 0 based in Hive and SparkSQL
In BigQuery, there are several ways to access a specific index
OFFSET: 0 Based & Error occurs when you access the index which exceeds the boundary of the array
ORDINAL: 1 Based & Error occurs when you access the index which exceeds the boundary of the array
SAFE_OFFSET: 0 Based & Return null when you access the index which exceeds the boundary of the array
SAFE_ORDINAL: 1 Based & Return null when you access the index which exceeds the boundary of the array
3.5.4. Handling date and timestamp
Extract current date and current timestamp
-- Extract current date and current timestamp
SELECT
-- if PostgreSQL, Hive, BigQuery
CURRENT_DATE as dt
, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP as stamp
-- if Hive, SparkSQL, BigQuery
-- CURRENT_DATE() as dt
-- , CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() as stamp
-- if Redshift
-- CURRENT_DATE as dt
-- , GETDATE() as stamp
-- if PostgreSQL, timestamp without timezone
, LOCALTIMESTAMP as local_stamp
;
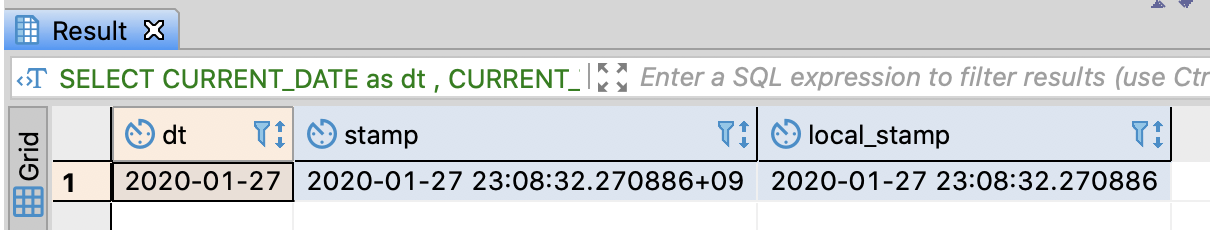
Generally, the functions related to timestamp return timestamp without timezone, while CURRENT_TIMESTAMP in PostgreSQL returns timestamp with timezone
In contrast, LOCALTIMESTAMP in PostgreSQL returns timestamp without timezone
In BigQuery, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP or CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() returns UTC time
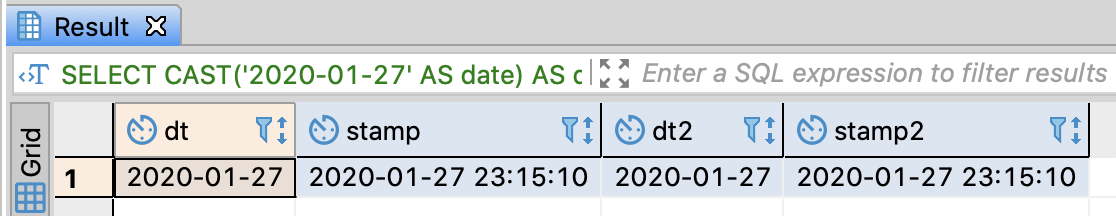
Convert string data type into date/timestamp
-- Convert string data type into date/timestamp
SELECT
-- if PostgreSQL, Hive, SparkSQL, Redshift, BigQuery
CAST('2020-01-27' AS date) AS dt
, CAST('2020-01-27 23:15:10' AS timestamp) AS stamp
-- if Hive, BigQuery
-- date('2020-01-27') AS dt
-- , timestamp('2020-01-27 23:15:10') AS stamp
-- if PostgreSQL, Hive, SparkSQL, Redshift, BigQuery. * Value must be not column name but constant value
-- date('2020-01-27') AS dt
-- , timestamp('2020-01-27 23:15:10') AS stamp
-- if PostgreSQL, Redshift
, '2020-01-27'::date AS dt2
, '2020-01-27 23:15:10'::timestamp AS stamp2
;
Extract a specific field from date/timestamp
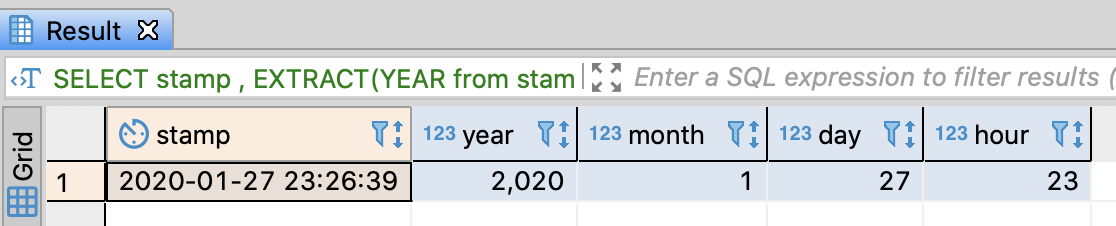
-- Extract a specific field from date/timestamp
SELECT stamp
-- if PostgreSQL, Redshift, BigQuery
, EXTRACT(YEAR from stamp) AS year
, EXTRACT(MONTH from stamp) AS month
, EXTRACT(DAY from stamp) AS day
, EXTRACT(HOUR from stamp) AS hour
-- if Hive, SparkSQL
-- , YEAR(stamp) AS year
-- , MONTH(stamp) AS month
-- , DAY(stamp) AS day
-- , HOUR(stamp) AS hour
FROM (SELECT CAST('2020-01-27 23:26:39' AS timestamp) AS stamp) AS t
;
3.5.5. Replace null with defaul value
- The result of arithmetic operation with NULL
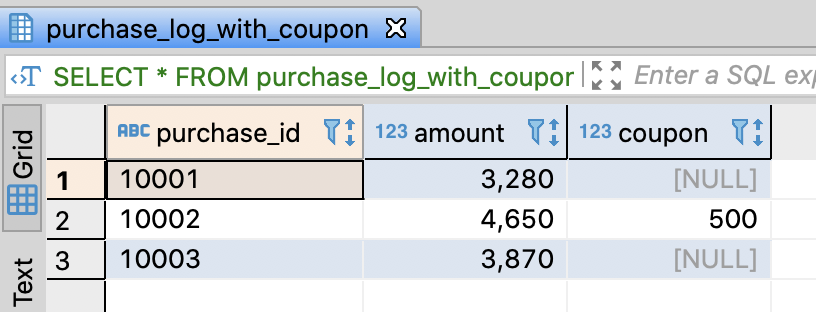
Create sample table and insert sample data
-- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS purchase_log_with_coupon;
-- Create purchage log table
CREATE TABLE purchase_log_with_coupon (
purchase_id varchar(255)
, amount integer
, coupon integer
);
-- Insert sample data
INSERT INTO purchase_log_with_coupon
VALUES
('10001', 3280, NULL)
, ('10002', 4650, 500)
, ('10003', 3870, NULL)
;
commit;
-- Select sample data
SELECT *
FROM purchase_log_with_coupon
;
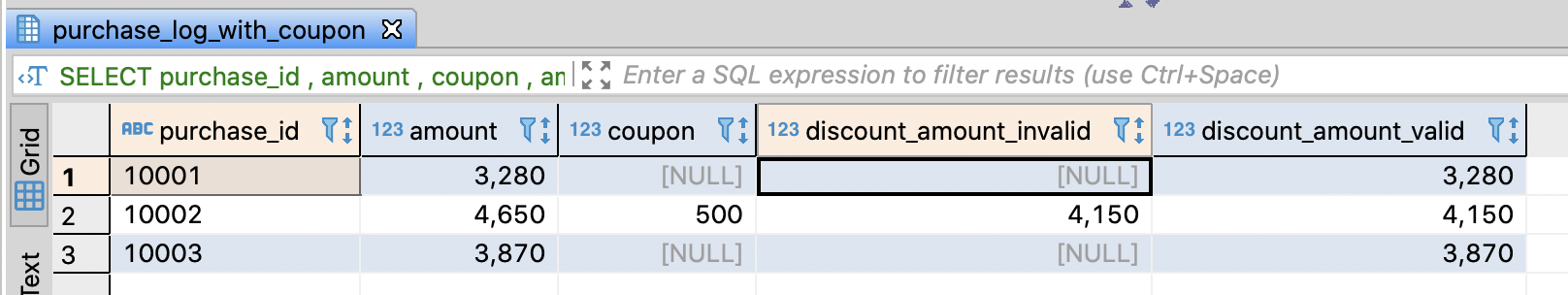
Compare the sum with null to the one with default value
-- Calculate the total sales except for coupon
SELECT purchase_id
, amount
, coupon
, amount - coupon AS discount_amount_invalid
, amount - COALESCE(coupon, 0) AS discount_amount_valid
FROM purchase_log_with_coupon
;
References
- 데이터 분석을 위한 SQL 레시피 - 한빛미디어
- HTTP Referer Wiki
댓글남기기