[Hive] New features on Hive 3.0
Goal
- The new features of Apache Hive 3.0
Practice
What’s new in this release: Apache Hive
- Apache Hive 3.0.0 was released on 21 May 2018 and the recent version is 3.1.2(based on 18 Feb 2020).
- One of the noticeable features is that Hive 3.0 supports seamless ACID(Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) and you have to consider serveral thing about the transactional tables created by a Hive version prior to Hive 3.
- Futhermore, several SQL features and useful connectors were added.
- And also, it enhance the performance through improved LLAP and Apache Spark.
Hive3 New Features
ACID v2
- Originally Hive supported write only by adding partitions or loading new file into existing partitions because HDFS Hive already has not allowed file replaced or edited.
- Hive had supported the trasactinons and INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE since 0.13 version was released. But it had several drawbacks like these.
- Transactional tables had to be stored in ORC and and bucketed
- Reading transactional tables was significnatly slower than non-transactional ones
- No support for MERGE or UPSERT funcionality
- Seamless INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE opertaions on existing tables and improve the performance just as good as non-ACID
- Transactional tables don’t have to be bucketed anymore
- Non-ORC format bales supported (INSERT & SELECT only)
- Compatibility with cloud storage providers
- eg. Amazon S3
- New HiveStreaming API (v2)
LLAP(Live Long And Process) workload management
- It consists of a long-lived daemon which replaces direct interactions with the HDFS DataNode, and a tightly integrated DAG-based framework.
- Functionality such as caching, pre-fetching, some query processing and access control are moved into the daemon. Small/short queries are largely processed by this daemon directly, while any heavy lifting will be performed in standard YARN containers.
- Live Long And Process (LLAP) functionality was added in Hive 2.0 and Hive 3.0 supports new features
- Split your LLAP resources in pools
- e.g. bi (for Business Analytics) and etl (for Extract Transform and Load)
- Automatically map applications to pools
- e.g. Tableau to the bi pool
- Create triggers to dynamically move applications from one pool to another
- e.g. move long running queries to the etl pool
- Activate/deactivate your resource plans based on your users’ needs (one active at a time).
- Split your LLAP resources in pools
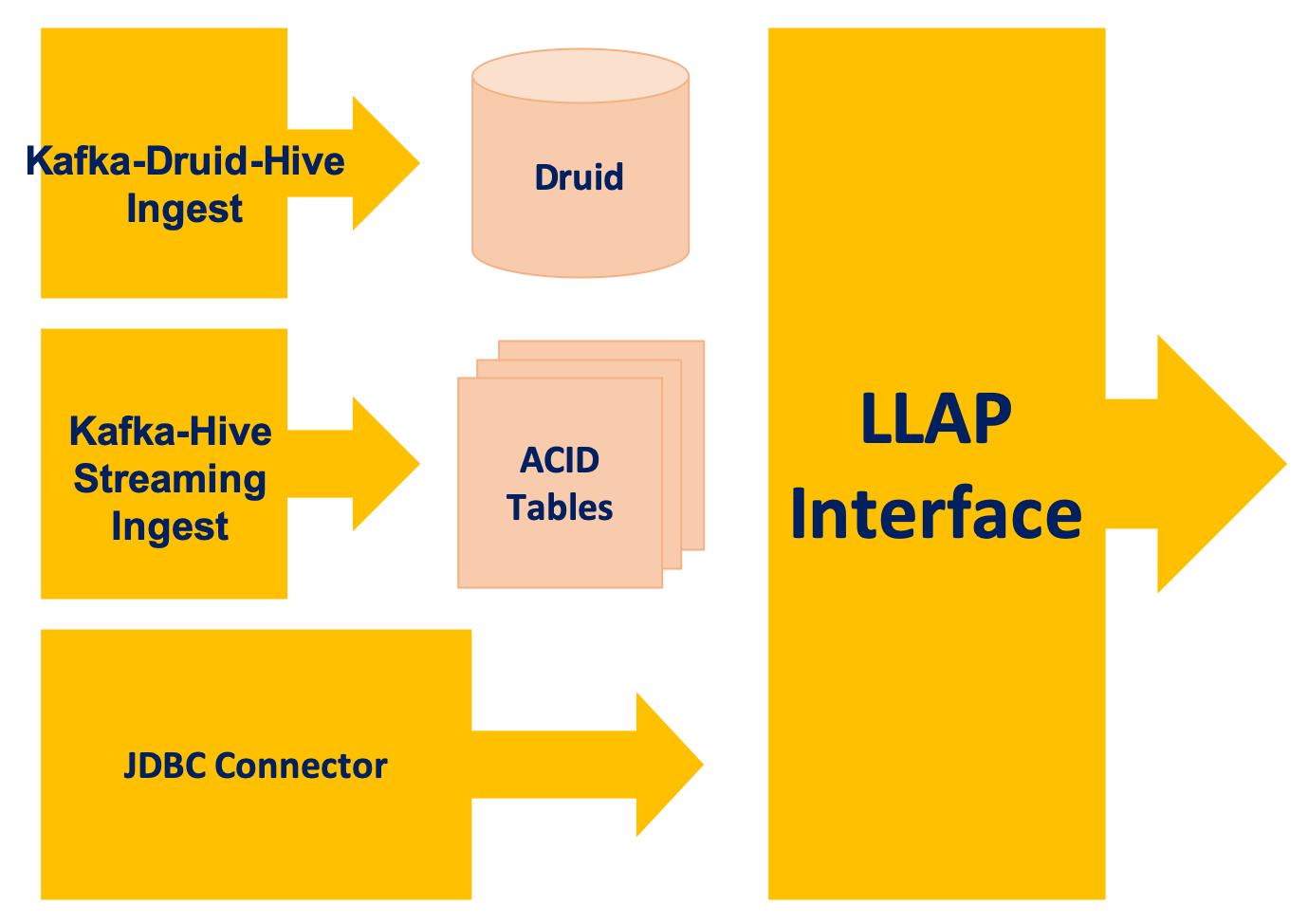
JDBC, Druid and Kafka connectors
- JDBC connector(JdbcStorageHandler)
- It is read-only for now.
- It allows you to easily read/import data from any of the supported databases.
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MSSQL and Apache Derby
- Kafka connector
- It can be used to query real-time data from Apache Kafka.
- You connect to Kafka data from Hive by creating an external table that maps to a Kafka topic.
- It can be used to achieve exactly-once offloading of data to Hive and real-time data transformation.
- The Hive-Kafka connector supports the following serialization and deserialization formats:
- JsonSerDe (default)
- OpenCSVSerde
- AvroSerDe
- Exactly-once ingestion from Kafka to Druid can be done through Hive.
- The Hive-Kafka connector supports the following serialization and deserialization formats:
- It can be used to query real-time data from Apache Kafka.
Hive Warehouse Connector for Apache Spark
- All interactions between Hive and Apache Spark has to go through the Hive Warehouse Connector.
- This connector takes advantage of Hive LLAP to allow streaming/ACID interaction between Hive and Spark.
- The Spark application will need to access a Hive Server Interactive (with LLAP activated) to read Hive managed tables, but it won’t need it to write to Hive managed tables or read/write Hive external tables.
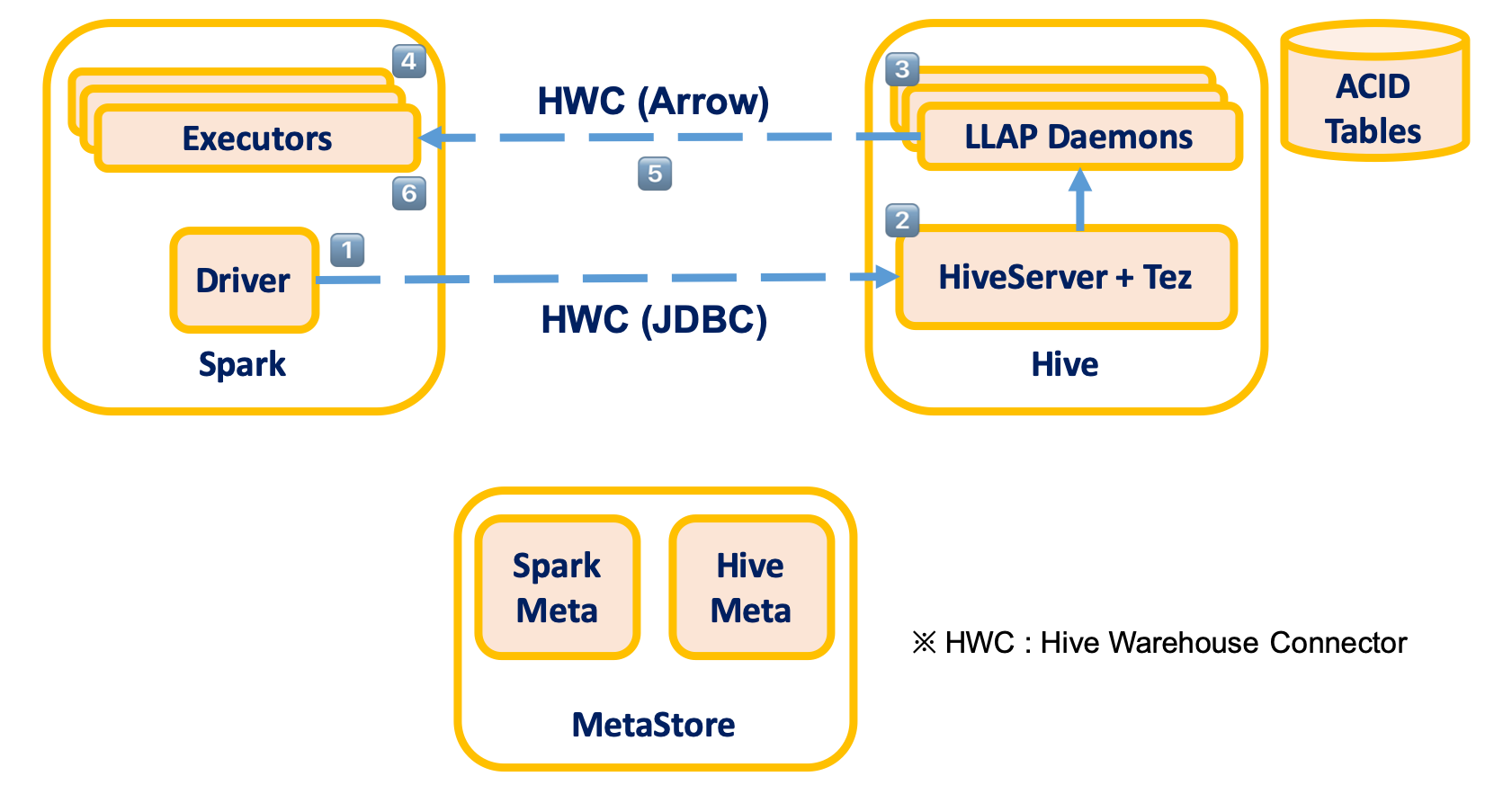
- Execute Query Process
-
- Driver submits query to HiveServer
-
- Compile query and return “splits” to Driver
-
- Execute query on LLAP
-
- Executor Tasks run for each split
-
- Tasks read Arrow data from LLAP
-
- HWC returns ArrowColumnVectors to Spark
-
SQL features
- Constraints and default values
- DEFAULT value for each column is available and it can be used in INSERT and UPDATE statements.
UNIQUE and NOT NULL SQL constraints and **PRIMARY FOREIGN KEY** already have been added in Hive 2.1
- DEFAULT value for each column is available and it can be used in INSERT and UPDATE statements.
- Tables information
- Hive 3 allows easy exploration of the whole warehouse with information_schema and sys databases.
Improved performance
- Based on a recent TPC-DS benchmark by the MR3 team, Hive LLAP 3.1.0 is the fastest SQL-on-Hadoop system available in HDP 3.0.1.
- The benchmark compares all the SQL systems embedded with HDP3 as well as Hive on MR3 (a new execution engine for Hadoop and Kubernetes), by running a set of 99 SQL queries.
| System | Total TCP-DS running time (seconds) |
|---|---|
| HDP 3.0.1 LLAP | 5516.89 |
| Hive 3.1.0/MR3 | 6575.052 |
| HDP 3.0.1 Tez | 12227.317 |
| Presto 0.208e | 12948.224 |
| Spark 2.3.1 | 26247.471 |
Materialized views (MV)
- It can improve the performance by serveral ways
#### Storage for intermediate results
- Materialized views results are stored, allowing mutualizing computing costs. #### Incremental rebuilding
- Updating an materialized view only computes the data that was inserted in its sources tables since the last update. ##### Query rewriting
- When appropriate, the cost-based optimizer uses existing materialized views to plan queries instead of the sources tables, without the user being aware of it.
Other features
- Surrogate Keys
- TIMESTAMP WITH TIMEZONE data type
- Apache Parquet and text files are supported in LLAP
댓글남기기