[OpenCV] What is the Mat?
Goal
- What is the mat
- How it works
- How to convert a matrix to a bytes array
- The method for storing image data
Intro
- I had a problem to diplay the image which was serialized.
- So, I need to understand how OpenCV handles the matrix exactly
Practice
Change of way to handle the image
- OpenCV 1.0
- C language base
- You have to manage the momory manually
- It use IplImage for handling the image
IplImage : C structure for storing the image in the memory
- OpenCV 2.0
- It introduce a new C++ interface
- Nevertheless, it is fully compatible with C
- No need to fiddle with the memory management
- However, a lot of embedded developments support only C
- As using the Mat, you don’t need to allocated and release the memory manually. This is because the Mat manages the memory automatically
Mat Structure
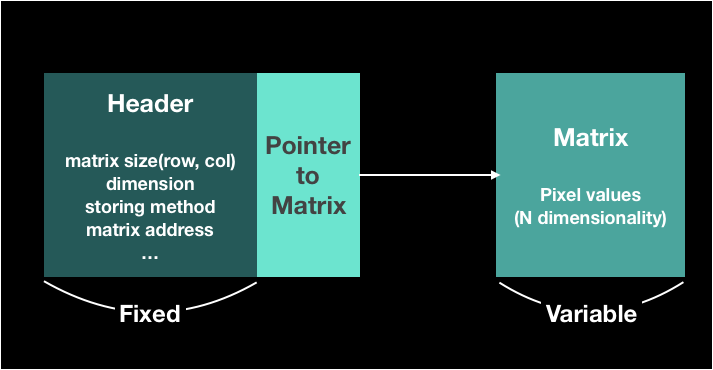
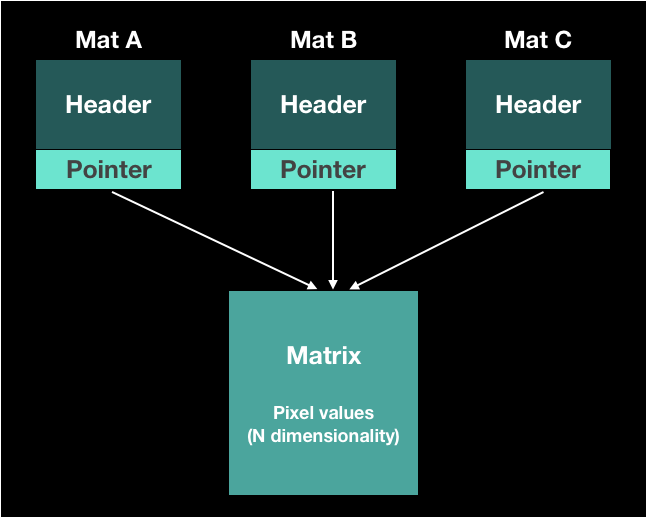
Sharing a matrix
- To solve the performance issue by unnecessary copies of potentially large images
- OpenCV uses a reference counting system
- It copy only header generally and support deep copy as well
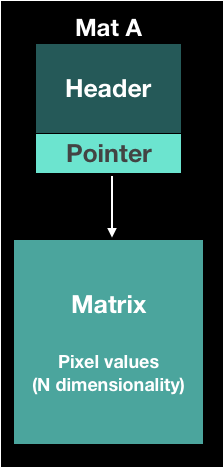
General Copy
Mat A = imread(...);
Mat B = Mat(A);
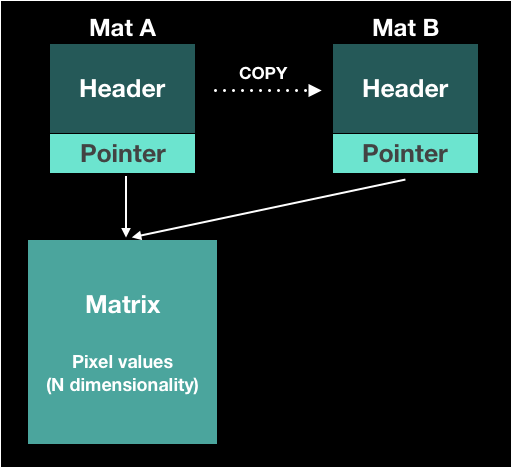
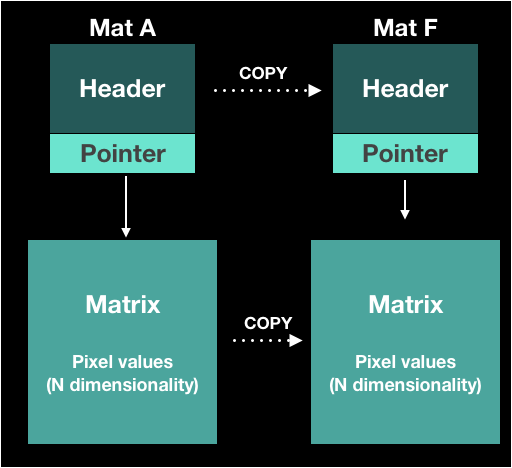
Deep Copy
- Copy not only heaer but also matrix
Mat F = A.clone();
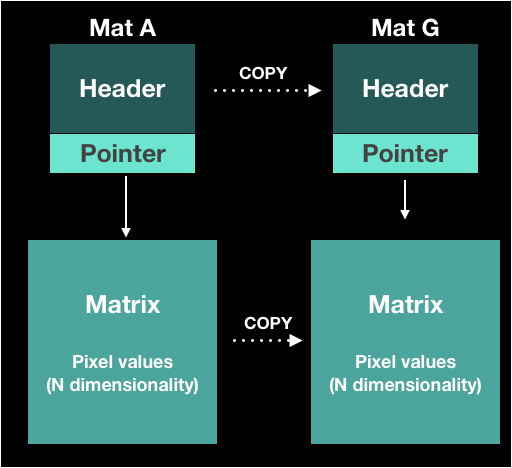
Mat G;
A.copyTo(G);
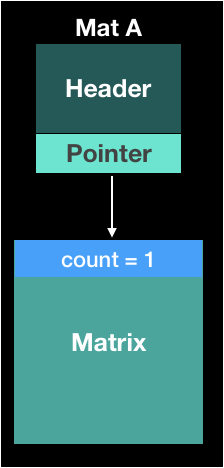
When a matrix object is free in the memory?
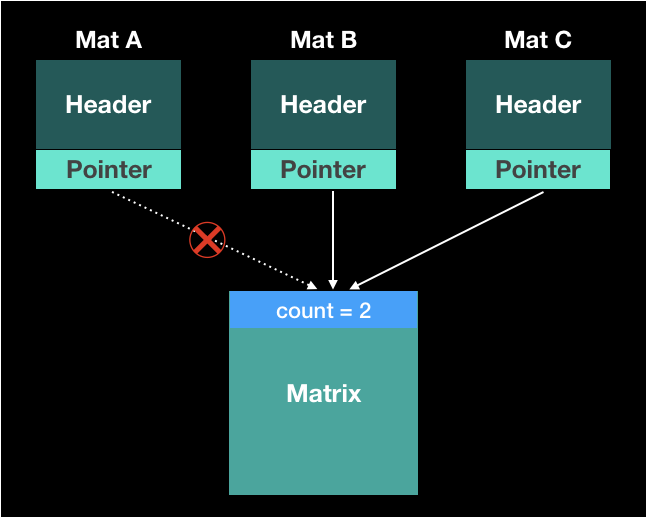
- I mentioned, OpenCV uses counting references
- So, If the count of pointers which indicate the matrix, it’ll be free automaticlly
Example
Mat a = imread(...);
Mat B = Mat(A);
Mat C = Mat(A);
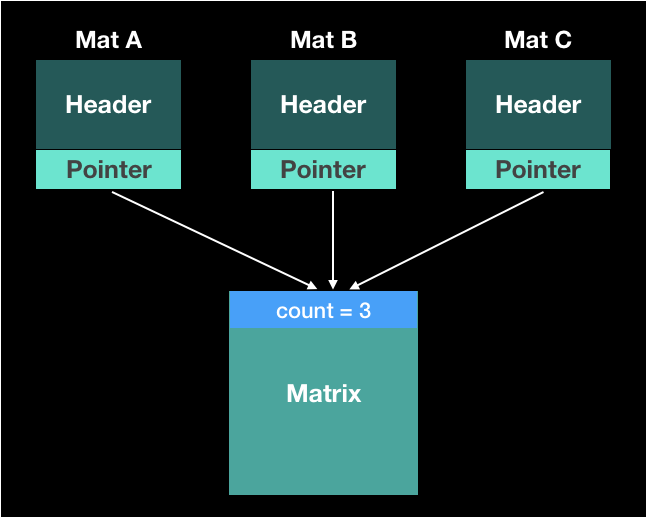
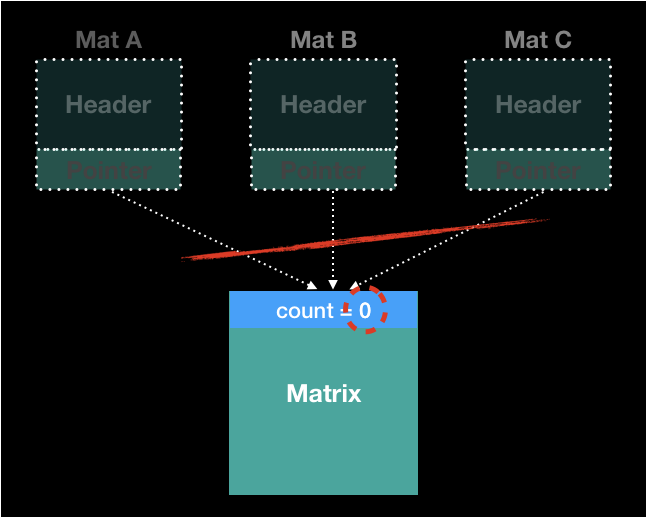
free(A);
free(B);
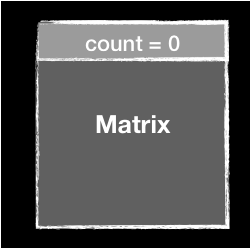
free(C);
Storing methods
Gray scale
- White/Black
- Create many shades of gray
RGB
- The most common method
- Similar to our eyes
HSV/HLS
- Decompose colors into hue/Saturation and value/luminance components
- More natural way to decribe colors
YCrCb
- Used by JPEG image format
The smallest data type of each component is char = 1 byte = 8 bits
value range of signed char is -127 and 127
value range of unsigned char is 0 ~ 255
Can use other types like float(4 bytes or 32 bits) and double(8 bytes or 64 bits) and they can provide ever finer control
However, the size of image will be increased as using them
Creating Mat
- Mat is a image container and also a general matrix class, that is, 2-dimentional marices
- Mat(row, column, store_method)
- Store method
- CV_[The number of bits per item] [Signed or Unsigned] __{[Type Prefix]}__C[The channel number]
eg. CV_8UC3 : Unsigned 8bits(unsigned char) and 3 channles
eg. CV_32UC1 : Unsigned 32bits(usigned float) and 1 channel
- Store method
How to store N-dimensions
- Convert N-dimensions matrices to 1-D aaray
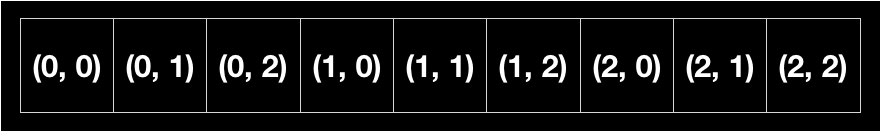
1-D Matrix to 1-D Array
-
eg. 3x3
-
Matrix

- Array(Bytes Array)
Contiguous
- The way to order the data in memory
- There are C-contiguous, Fortran-contiguous and so on
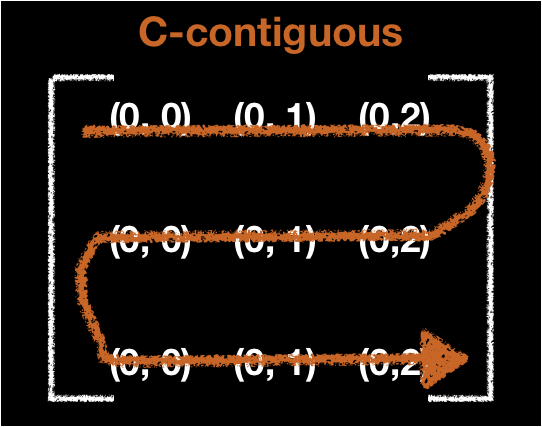
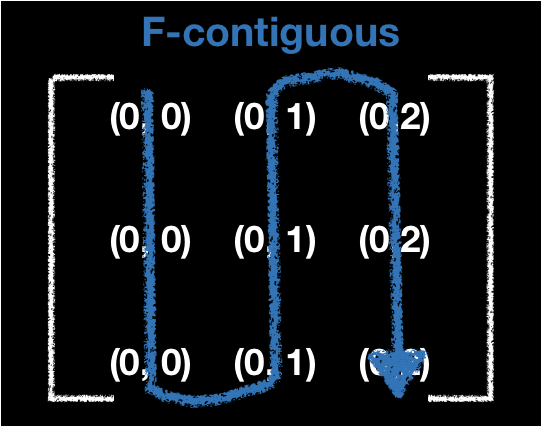
N-d Matrices to 1-D Array
-
eg. RGB(CV_8UC3/) 3-Dimensions
-
Matrices
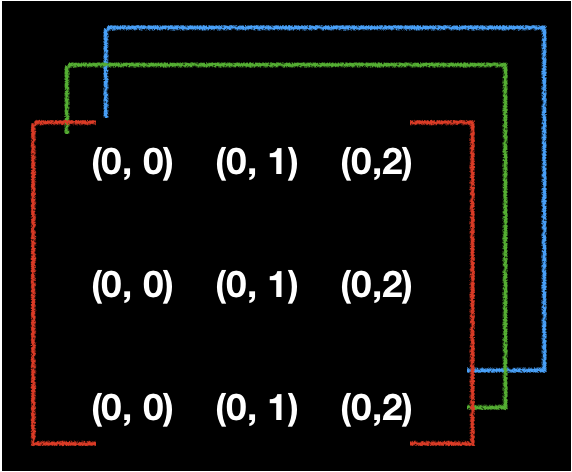
- Array(Bytes Array)

Mat manages RGB as BGR
댓글남기기